The UAE’s e-invoicing mandate starting in 2026 has created uncertainty among business owners who need clear guidance on implementation timelines and requirements. Many are asking: “When exactly do I need to implement e-invoicing for my business, and what’s the step-by-step roadmap to ensure compliance?”
The Federal Tax Authority (FTA) has established a comprehensive phase-wise implementation schedule that varies based on business size, transaction volume, and sector classification. This structured rollout approach aims to ensure smooth transition while minimizing business disruption across the UAE’s diverse economic landscape.
Understanding the complete implementation roadmap helps businesses plan their e-invoicing adoption strategy, allocate resources effectively, and ensure timely compliance while avoiding penalties and operational challenges during the transition period.
What Is the FTA Timeline and Phase-Wise Rollout Schedule?
The FTA has designed a structured phase-wise rollout schedule spanning from July 2026 to December 2027, with different implementation deadlines based on business characteristics and readiness levels. This graduated approach ensures manageable transition while maintaining system stability and compliance quality.
The rollout schedule prioritizes large enterprises and high-volume businesses in the initial phases, followed by medium-sized businesses, and concludes with small businesses and specialized sectors. Each phase includes preparation periods, testing phases, and mandatory go-live dates that businesses must meet.
How Are the Implementation Phases Structured?
| Phase | Timeline | Target Businesses | Key Requirements | Preparation Period |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phase 1 | July 2026 – September 2026 | Large enterprises (>AED 500M revenue) | Full system integration, real-time reporting | 18 months advance preparation |
| Phase 2 | October 2026 – December 2026 | Medium-large businesses (AED 100M-500M) | Standard integration, automated processing | 15 months advance preparation |
| Phase 3 | January 2027 – March 2027 | Medium businesses (AED 25M-100M) | Simplified integration, basic automation | 12 months advance preparation |
| Phase 4 | April 2027 – June 2027 | Small-medium businesses (AED 5M-25M) | Streamlined solutions, assisted implementation | 9 months advance preparation |
| Phase 5 | July 2027 – September 2027 | Small businesses (<AED 5M) | Basic solutions, support programs | 6 months advance preparation |
| Phase 6 | October 2027 – December 2027 | Specialized sectors, exempted categories | Sector-specific requirements | Ongoing support |
This structured approach ensures adequate preparation time while providing businesses with clear deadlines and implementation support based on their operational complexity and resource capabilities.
What Preparation Activities Should Begin in Each Phase?
Preparation activities vary by phase but include system assessment, vendor selection, integration development, staff training, and compliance testing that must be completed before mandatory go-live dates. Early phases require more comprehensive preparation due to complex integration requirements.
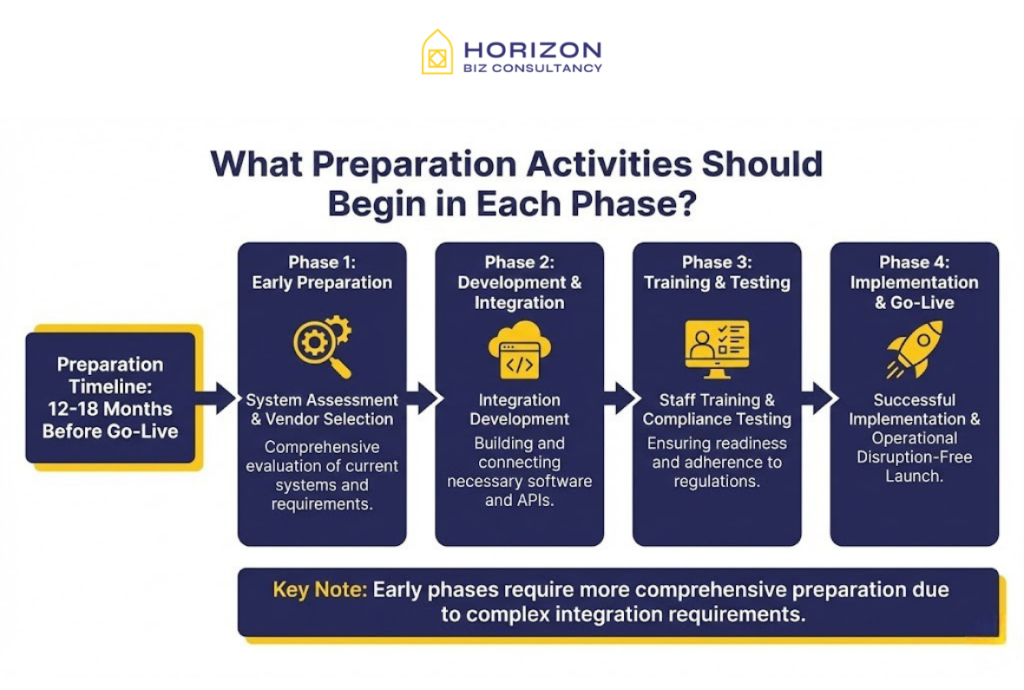
Businesses should begin preparation 12-18 months before their designated phase to ensure adequate development time, testing cycles, and staff training that supports successful implementation without operational disruption.
How Does the FTA Support Businesses During Each Phase?
The FTA provides phase-specific support including technical guidance, compliance resources, testing environments, and implementation assistance that helps businesses navigate their e-invoicing adoption successfully. Support levels increase for smaller businesses with limited technical resources.
What Are the Mandatory vs Voluntary Compliance Periods?
The UAE e-invoicing implementation includes voluntary early adoption periods followed by mandatory compliance deadlines that provide businesses with flexibility while ensuring universal adoption by specified dates.
Voluntary periods allow businesses to implement e-invoicing before their mandatory deadline, gaining operational benefits and compliance experience. Mandatory periods require full compliance with penalties for non-adoption, ensuring complete market transition.
How Do Voluntary and Mandatory Periods Work?
| Compliance Type | Duration | Business Benefits | Requirements | Support Available |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voluntary Early Adoption | 12-18 months before mandatory | Testing opportunities, competitive advantage | Optional compliance, partial implementation | Enhanced support, testing resources |
| Voluntary Full Implementation | 6-12 months before mandatory | Operational benefits, reduced rush | Complete system integration | Technical assistance, training programs |
| Mandatory Compliance | Phase-specific deadlines | Legal requirement fulfillment | Full compliance, no exceptions | Standard support, penalty avoidance |
| Post-Implementation | Ongoing after go-live | Continuous improvement, optimization | Maintained compliance, updates | Ongoing support, enhancement guidance |
Understanding these periods helps businesses optimize their implementation timeline while leveraging available support and avoiding compliance pressures.
What Advantages Do Businesses Gain from Early Voluntary Adoption?
Early voluntary adoption provides competitive advantages including system optimization time, staff training opportunities, operational efficiency improvements, and reduced implementation pressure that support smoother transition and better long-term outcomes.
Voluntary adopters also receive enhanced FTA support, access to testing environments, and priority assistance that facilitates successful implementation while avoiding the resource constraints of mandatory deadline periods.
What Penalties Apply During Mandatory Compliance Periods?
Mandatory compliance periods include penalty structures for non-compliance, late implementation, and system failures that enforce universal adoption while providing reasonable implementation timeframes. Penalties escalate based on delay duration and business size.
How Does Business Size Categorization Affect Implementation Deadlines?
Business size categorization directly determines implementation deadlines, with larger enterprises required to adopt e-invoicing earlier due to their greater transaction volumes and system capabilities. This approach ensures systematic market transition while accommodating different business capacities.
The categorization considers annual revenue, transaction volume, employee count, and operational complexity that influence implementation timeline assignments and support requirements.
How Are Businesses Classified Into Size Categories?
Businesses are classified based on their latest audited financial statements, VAT registration details, and transaction history that determines their appropriate size category and implementation timeline. Classification considers multiple factors to ensure accurate categorization.
The FTA uses automated classification systems combined with business self-declaration to assign appropriate categories, with appeals processes available for businesses requiring reclassification.
What Support Is Available for Different Business Sizes?
Different business sizes receive tailored support including technical assistance levels, implementation resources, and training programs that match their operational capabilities and resource constraints.
What Technical Infrastructure Requirements Must Businesses Meet?
Technical infrastructure requirements vary by business size and implementation phase, encompassing system capabilities, integration standards, security protocols, and operational readiness that ensure successful e-invoicing adoption.
Infrastructure requirements include hardware specifications, software capabilities, network connectivity, security measures, and backup systems that support reliable e-invoicing operations and compliance maintenance.
What Are the Core Infrastructure Components?
| Infrastructure Component | Minimum Requirements | Recommended Specifications | Business Size Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| System Integration | API connectivity, data validation | Real-time processing, automated workflows | Scales with transaction volume |
| Security Infrastructure | Encryption, authentication | Multi-layer security, monitoring | Enhanced for larger businesses |
| Data Storage | Structured databases, backup systems | Redundancy, disaster recovery | Capacity matches business size |
| Network Connectivity | Reliable internet, bandwidth | High-availability connections | Redundancy for critical operations |
| Processing Capacity | Transaction handling capability | Scalable processing power | Matches peak transaction loads |
Infrastructure planning should consider current needs and future growth to ensure long-term system adequacy and compliance sustainability.
How Should Businesses Plan Their Infrastructure Upgrades?
Infrastructure upgrade planning should begin with current system assessment, future requirement forecasting, and phased improvement implementation that aligns with e-invoicing deadlines while supporting business growth. Planning includes vendor evaluation, cost-benefit analysis, implementation scheduling, and testing protocols that ensure infrastructure readiness for e-invoicing compliance.
What Staff Training and Change Management Is Required?
Staff training and change management are critical success factors for e-invoicing implementation, requiring comprehensive programs that address technical skills, process changes, and compliance requirements across all relevant business functions.
Training needs include system operation, compliance procedures, troubleshooting capabilities, and change adaptation that ensure staff readiness for new e-invoicing workflows and requirements.
What Vendor Selection and Implementation Support Options Are Available?
Vendor selection for e-invoicing implementation involves evaluating solution providers based on FTA compliance, integration capabilities, support quality, and long-term partnership potential that ensures successful system deployment and ongoing operations.
Available options include comprehensive solution providers, specialized integration services, cloud-based platforms, and hybrid solutions that cater to different business sizes and requirements.
How Should Businesses Evaluate E-Invoicing Solution Providers?
| Evaluation Criteria | Key Considerations | Assessment Methods | Decision Factors |
|---|---|---|---|
| FTA Compliance | Certified solutions, regulatory adherence | Compliance verification, testing results | Mandatory requirement |
| Integration Capabilities | System compatibility, API quality | Technical assessment, pilot testing | Implementation feasibility |
| Support Services | Training, maintenance, troubleshooting | Service level agreements, references | Long-term partnership |
| Scalability | Growth accommodation, feature expansion | Capacity testing, roadmap review | Future business needs |
| Cost Structure | Implementation, licensing, ongoing costs | Total cost analysis, ROI calculation | Budget alignment |
Thorough vendor evaluation ensures selection of appropriate solutions that meet current needs while supporting future business growth and compliance requirements.
What Implementation Support Services Should Businesses Expect?
Implementation support services should include project management, technical integration, staff training, testing assistance, and go-live support that ensures successful e-invoicing deployment with minimal business disruption.
Quality support providers offer comprehensive services from initial planning through post-implementation optimization, ensuring businesses achieve successful e-invoicing adoption and ongoing compliance.
Conclusion
The UAE E-Invoicing Mandate 2026 requires systematic preparation and implementation planning that aligns with FTA’s phase-wise rollout schedule and business-specific requirements. Understanding the complete implementation roadmap enables businesses to prepare adequately, allocate resources effectively, and ensure timely compliance while leveraging the benefits of digital transformation.
Successful e-invoicing implementation depends on early preparation, appropriate vendor selection, comprehensive staff training, and adequate infrastructure development that supports both compliance requirements and operational efficiency. Businesses that follow the structured implementation roadmap will achieve smooth transition while gaining competitive advantages through improved operational capabilities.
The key to successful e-invoicing adoption lies in understanding your business category, preparing according to the designated timeline, and leveraging available support resources to ensure compliance readiness and operational excellence.
FAQ’s
Businesses should begin preparation 12-18 months before their designated phase deadline, with large enterprises starting January 2025 and smaller businesses beginning preparation based on their size category timeline.
Yes, businesses can adopt e-invoicing voluntarily before their mandatory deadline, gaining operational benefits and implementation experience while receiving enhanced FTA support and testing resources.
Non-compliance with implementation deadlines may result in penalties, operational restrictions, and compliance issues. Early preparation and vendor support help ensure timely implementation.
Business size categories are determined based on annual revenue, transaction volume, and operational complexity using audited financial statements, VAT registration details, and transaction history.
Small businesses receive enhanced support including simplified solutions, assisted implementation, extended preparation periods, and specialized training programs designed for limited technical resources.





